Your company can save thousands of valuable hours by integrating business operations and eliminating manual tasks. Many businesses face challenges with disconnected systems as their competitors move ahead with efficient processes.
Cloud computing, data analytics, and automation have changed the way companies operate. Business operations technology has become crucial for survival, especially with data breach costs reaching £3 million in 2021. Companies that adopt business operations solutions like Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems can connect vital functions. These systems unite finance and supply chain management teams and improve communication across departments.
Our research into the digital transformation scene reveals seven powerful tools with proven results. These solutions help businesses of all sizes concentrate on growth instead of administrative burdens. Smart tools like robotic process automation handle routine data entry tasks while modern accounting systems provide immediate financial insights. Your operational efficiency will improve significantly with these innovations.
Process Automation Tools
Image Source: Umbrex
Process automation tools play a vital role in creating optimized integrated business operations. These tools help organizations cut down on manual tasks. McKinsey & Company’s research shows that 60% of all jobs worldwide could automate up to 30% of their activities. This shows how much potential these tools bring to the table.
Process Automation Tools key features
Different types of business process automation tools are available. Each type has unique capabilities that boost integrated business operations:
IT Process Automation (ITPA) tools came from batch scheduling tech of the 1960s. Today’s ITPA solutions give IT teams visual workflow designers and API access. This lets them build processes to handle data across different systems. The main features are:
- Advanced analytics with detailed views and automated logging
- Dynamic resource provisioning
- Event-based automation triggers
- Up-to-the-minute monitoring and alerts
Business Process Automation (BPA) platforms grew from business process management technology. They help develop, automate, and track complex processes crucial to business operations. You’ll find these features:
- No-code and low-code development interfaces
- Workflow management capabilities
- Document processing features
- End-to-end automation and orchestration
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) tools work through user interfaces. They automate repetitive, rule-based tasks like data collection and entry. These tools shine when handling structured, rule-based, high-volume tasks where human input adds little value.
Digital Process Automation (DPA) blends ITPA and BPA elements. This helps streamline end-to-end data delivery that supports customer experiences.
Process Automation Tools pros and cons
Pros:
- Improved efficiency: PNC Financial Services Group cut manual workload by 80% when reviewing bank loan applications after automation.
- Time savings: Paper processes run 30-40% faster after automation. This speeds up time-to-market.
- Error reduction: Carlsberg Danmark’s business process automation cut order processing time by over 90%. They also wiped out almost all errors.
- Better scalability: Automated processes adapt easily to growing demands. Companies can respond better to market changes.
- Better compliance: Automation helps meet strict data security standards and regulatory requirements smoothly.
Cons:
- Big upfront costs: Setting up automated systems can cost millions.
- More maintenance: Automated equipment needs more upkeep than manual machines.
- Complex setup: Poor planning of business process automation can make enterprise operations more complicated.
- Job losses: Forrester Research says AI will make 7% of jobs obsolete. This could hurt employee morale and company image.
- Less flexible: Even the most flexible automation systems can’t match human adaptability.
Process Automation Tools pricing
Each vendor has its own pricing approach:
IBM gives you a 30-day free trial for their Robotic Process Automation solution. After that, you can choose between SaaS or on-premises with custom pricing.
Microsoft Power Automate costs about $15 monthly per user for attended RPA. The Process package with unattended automation runs $150 monthly.
Automation Anywhere’s Cloud Starter Pack starts at $750 monthly. This gives you one bot creator, control room, and unattended bot. Extra unattended bots cost $500 monthly each. Attended bots run $125 monthly per user.
UiPath’s Pro package costs $420 monthly. You get 25 licenses, one attended bot, one unattended bot, one action center, and one orchestrator.
Argos Labs charges $6,000 yearly for their base package. This includes one developer account and three bots for development, testing, and deployment.
Process Automation Tools best use cases
These tools excel in many business areas:
Finance and Accounting:
- Invoice processing with automatic data extraction
- Customer invoicing with clear routing
- Expense reimbursement with quick approval workflows
Human Resources:
- Employee onboarding to speed up productivity
- Benefits enrollment with automatic reminders
- Vacation requests with simple approval processes
Information Technology:
- System integration and migration
- Password resets for approved users
- Server and application monitoring
Customer Service:
- Support ticket routing based on skills and availability
- Automated case management
- Customer request handling
Supply Chain Management:
- Faster procurement processes
- Quality control data collection
- Trend spotting through process dashboards
Companies should start by finding repetitive, rule-based tasks that automation could improve. A cost-benefit analysis helps decide if the benefits outweigh setup costs. The final choice lies between complete business process redesign or partial automation of current processes.
Process automation forms the backbone of integrated business operations. It cuts costs and lets people focus on strategic, value-adding work.
Cloud-Based Collaboration Platforms

Image Source: Cflow
Cloud collaboration platforms have transformed how teams work together. They are a significant part of integrated business operations for companies looking to stay flexible and improve. About 90% of companies now move their workflows to the cloud. These platforms make shared work possible through websites, mobile apps, or desktop software, whatever the team’s location.
Cloud-Based Collaboration Platforms key features
Cloud collaboration tools have several core features that make integrated business operations work:
Real-time collaboration lets multiple users edit documents, spreadsheets, or presentations at the same time. Teams can make decisions faster because everyone works with current information, which eliminates version control problems.
File sharing and storage gives teams a central, flexible place to securely access, store, and share files. This breaks down information silos and creates a single source of truth for all business data.
Integrated communication tools combine instant messaging, video conferencing, and commenting in one platform. Teams can discuss ideas, give feedback, and clarify project details without switching between apps.
Version control keeps track of document changes, showing who made modifications and when. Teams can restore previous versions if needed, which protects document integrity and prevents data loss.
Access control lets administrators set custom permission levels to decide who can view, edit, or comment on specific documents. This detailed control keeps sensitive information secure while allowing necessary collaboration.
Cloud-Based Collaboration Platforms pros and cons
Pros:
- Better productivity: Cloud platforms simplify processes and cut delays from traditional communication methods. Organizations see up to 35% improvement through workflow automation.
- Better communication: Teams can communicate in real-time whatever their location, which encourages transparency and leads to better project outcomes.
- Cost-effectiveness: Subscription models eliminate big upfront hardware and software investments, which reduces IT costs.
- Flexibility: Team members can access files and work together from any device with internet connectivity, which supports remote and hybrid work.
- Scalability: Cloud resources adjust easily to match changing business needs without disruption.
Cons:
- Internet dependency: Cloud collaboration needs stable internet connections, which can cause access problems during outages.
- Security concerns: Data breaches remain a risk despite strong security measures.
- Learning curve: New software often requires extra training and support.
- Decision-making delays: Multiple viewpoints can make reaching consensus take longer.
- Resistance to change: Some employees might resist new collaboration methods, which can affect implementation success.
Cloud-Based Collaboration Platforms pricing
Cloud collaboration platforms typically use subscription-based pricing:
Microsoft 365’s cloud productivity suite includes an integrated employee experience platform (Viva) with various pricing tiers based on features and user numbers.
Google Workspace uses a pay-as-you-go model where customers pay only for services they use, without upfront fees or termination charges. Committed use discounts can save up to 57%.
Slack’s workflow automation capabilities help organizations save about 35% of their time.
Most platforms offer tiered pricing from free basic plans to premium enterprise options:
- Free: Simple collaboration tools with limited storage
- Basic: $5/user/month with enhanced storage and standard support
- Standard: $10/user/month with advanced features and improved security
- Premium: $20/user/month with unlimited storage and priority support
- Enterprise: Custom pricing with dedicated support and compliance features
Cloud-Based Collaboration Platforms best use cases
Cloud collaboration platforms excel in several business scenarios:
Remote and hybrid work environments benefit from tools that enable uninterrupted communication and file sharing. Teams stay productive outside traditional office settings.
Cross-departmental projects work better with platforms that unite expertise from teams of all types. These tools provide clear workflow visibility and centralize project communications.
Client collaboration improves through secure external sharing features. Partners and customers can join projects while sensitive information stays protected.
Document-intensive processes like contract management, content creation, and financial reporting become easier with co-editing features and version control.
Training and knowledge sharing improves in collaborative workspaces. Teams create, share, and update resources to maintain consistent information across the organization.
Cloud collaboration platforms connect people, processes, and information in ways that improve operations and drive innovation.
Integrated CRM Systems
Image Source: Capsule CRM
CRM tools are the foundations of successful integrated business operations that connect front-office activities with back-end processes. Today’s CRM systems have grown beyond simple contact databases into complete platforms that bring customer data together from every touchpoint.
Integrated CRM Systems key features
Effective CRM systems provide robust contact management capabilities to organize vital information about current and potential customers in one available location. The system creates a single source of truth to discover the potential of previously trapped data, so team members can quickly find what they need.
Modern CRMs now use artificial intelligence to boost productivity and deliver deeper business insights. These AI-powered features improve sales forecasting and lead prioritization while they handle routine tasks automatically.
The most valuable CRM systems offer smooth third-party integrations with ERP systems, e-commerce platforms, and marketing tools. Data flows automatically between systems when integrated properly, which eliminates manual data entry and reduces human error.
Essential features include:
- Cloud-based accessibility so employees can find customer information anywhere
- Automation workflows that let employees focus on higher-value projects
- Live analytics providing applicable information from centralized data sources
- Mobile compatibility giving access on any device whatever the location
Integrated CRM Systems pros and cons
Pros:
An integrated CRM creates a unified platform where sales, customer service, and marketing teams can cooperate effectively with accurate, current information. Teams can break down data silos and make informed decisions based on complete customer insights.
CRM integration creates the groundwork to automate tasks like data entry, invoicing, and inventory tracking. Teams can focus on higher-value activities because automation reduces human error.
Companies that implement integrated CRMs report better customer experiences through tailored follow-ups and customized offerings that match customer needs. CRM integrations help 59% of organizations improve their close rates.
Cons:
Ready-made CRM systems don’t deal very well with all company requirements. Limited customization options can reduce effectiveness in specific business situations. Companies that use such solutions often depend on the provider for updates, technical support, and system development.
Original costs of ready-made CRM systems are lower, but subscription fees add up over time. This is a big deal as it means that the total cost might exceed the one-time cost of a dedicated system. Businesses lose about $9.70 million yearly due to poor data quality, which shows why proper implementation matters.
Integrated CRM Systems pricing
CRM pricing follows subscription-based models that change based on features and user count. Most platforms offer tiered options from simple to enterprise-level packages.
To cite an instance, many CRM vendors offer free trials or basic versions before paid subscriptions. Higher-tier subscriptions include premium features like advanced analytics, automation capabilities, and unlimited storage.
Enterprise-level packages come with custom pricing based on business needs, dedicated support and enhanced security features. Integration capabilities with other business systems affect pricing, and some vendors charge extra for advanced integration options.
Integrated CRM Systems best use cases
Integrated CRMs shine when data needs to flow smoothly between customer-facing activities and back-end operations. Sales teams can see complete customer histories, which enables tailored interactions and better upselling opportunities.
Marketing departments exploit CRM data to spot market trends and interested customers in different product lines. Teams can run targeted campaigns and measure results directly against sales outcomes.
Customer service teams get a complete view of customer interactions across all channels, which streamlines support and reduces churn. This 360-degree customer perspective helps companies fix issues before they affect satisfaction.
To summarize, integrated CRM systems are vital components of successful integrated business operations. They connect customer information with essential business processes to create a unified ecosystem that drives productivity and strengthens customer relationships.
Business Intelligence and Analytics Tools
Image Source: GeeksforGeeks
Data-driven decision making powers effective integrated business operations. Business intelligence tools turn raw information into practical insights. These platforms help companies see complex data patterns, spot trends, and make smart strategic decisions.
Business Intelligence and Analytics Tools key features
Modern BI tools have several core features that drive integrated business operations:
Data visualization turns complex information into interactive charts, graphs, and maps. This makes it easy to spot hidden patterns and trends. Executives can quickly understand data through dashboards that show personalized, simple KPIs.
Advanced analytics lets businesses handle complex data through regression analysis, what-if scenarios, and statistical functions. These tools answer important business questions by giving practical insights that improve daily work.
Real-time data processing acts as a catalyst for business operations technology. Companies can now respond to market changes and customer behaviors quickly. This feature matters a lot for organizations that need fast decisions.
Self-service analytics puts data in everyone’s hands, whatever their technical skills. This availability builds a data culture while keeping security and governance intact.
Augmented analytics uses machine learning to boost data profiling and quality. It spots anomalies, finds new data segments, and uncovers key insights before active exploration.
Business Intelligence and Analytics Tools pros and cons
Pros:
- Enhanced clarity of data makes information easier to understand
- Better operational efficiency through faster reporting
- Better customer experience from understanding behavior
- Happy employees thanks to automated analysis tasks
- Edge over competitors by understanding market trends better
Cons:
- Original setup costs can be high, including licenses, infrastructure, integration, and training
- Staff resistance to changing their usual work methods
- Lack of data skills might need extra training
- Security risks when handling sensitive data
- Too much information can slow down decisions
Business Intelligence and Analytics Tools pricing
BI tools come with subscription-based or perpetual licensing:
Subscription-based pricing has three tiers:
- Entry-level (1-10 users): Up to $205/month with standard features
- Mid-tier (10-100 users): Up to $1,507/month with advanced capabilities
- High-end (100+ users): Up to $7,988/month with unlimited features
Popular platforms have different prices:
- Microsoft Power BI: Free Desktop version, Pro at $10/user/month, Premium starts at $4,995/month
- Tableau: Creator at $75/user/month, Explorer at $42/user/month, Viewer at $15/user/month
- IBM Cognos Analytics: Standard plan at $10/user/month, Premium at $40/user/month
Extra costs may include data migration, training, hardware, IT support, and maintenance.
Business Intelligence and Analytics Tools best use cases
BI tools shine in several integrated business operations areas:
Sales and revenue analysis helps businesses spot market trends and interested customers across product lines. Companies can create better upselling opportunities and targeted marketing campaigns.
Customer analytics and segmentation reveals buying behavior, shows cross-selling chances, and lifts customer satisfaction through feedback-based changes.
Financial performance analysis shows ways to save costs and boost profit margins by finding areas that need work. Companies can plan future budgets more effectively.
Operational efficiency monitoring watches key performance indicators, finds bottlenecks, and makes departments work better. BI dashboards show real-time performance across the company.
Supply chain optimization learns from data across procurement, processing, and distribution to make operations better. This helps fix inefficiencies and improve logistics in integrated business operations.
Business intelligence tools give a complete, current view of all important business data. Organizations can keep their operations running smoothly through better decision-making.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems
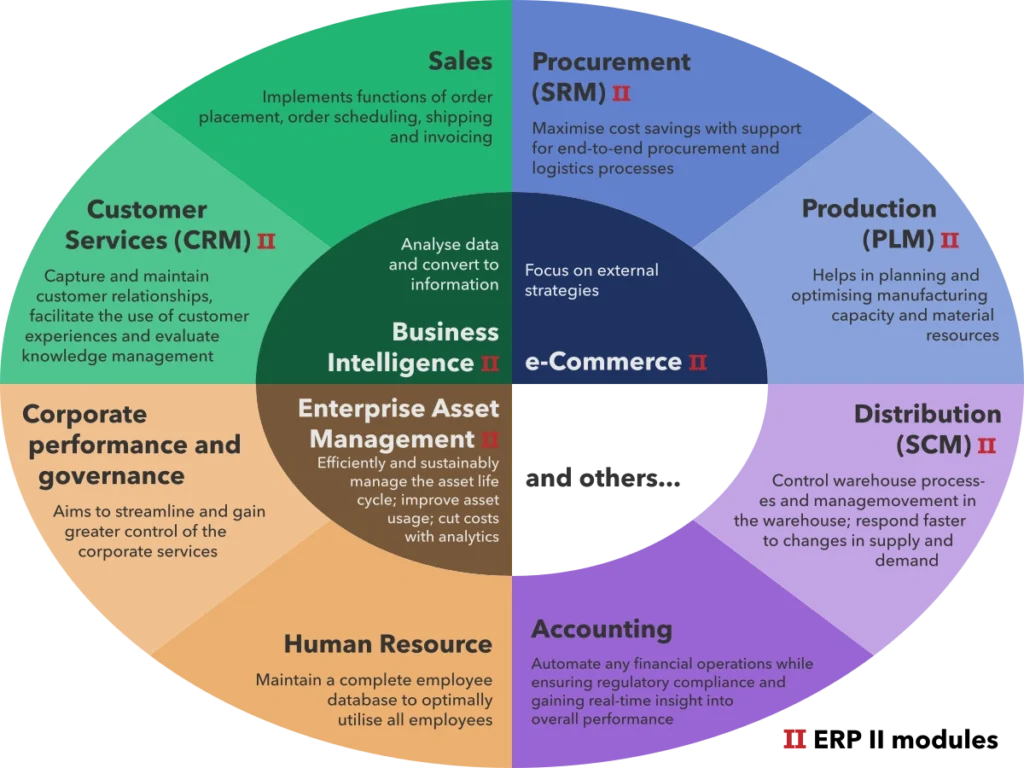
Image Source: Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems act as the central nervous system of integrated business operations. They unite different functions into one ecosystem. These detailed platforms build a foundation that allows information to flow smoothly through organizations of all sizes.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems key features
ERP systems offer unmatched integration through a central database. Users can define data once and apply it consistently across departments. This setup breaks down silos and allows live operations where teams can spot and fix problems quickly.
Core ERP capabilities include:
- Financial management – Simplifies everything from accounts payable to tax compliance with live financial data
- Supply chain management – Shows complete visibility into procurement, logistics, and inventory
- Human resources – Takes care of the entire employee lifecycle from recruitment to payroll
- Automation – Cuts manual tasks, reduces errors, and lets employees focus on strategic work
Modern cloud ERP solutions use AI, machine learning, and IoT technologies to boost efficiency and help make smarter decisions.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems pros and cons
ERP systems bring major benefits to business operations technology. They deliver live data reporting with custom metrics across functions. The platforms also make shared work easier by merging applications and data storage into one solution.
The challenges of ERP implementation are substantial. Original costs can be too high, particularly for smaller companies. Project timelines often run longer than expected because of customization needs and technical issues. Security remains a concern since centralized systems can attract cyberattacks.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems pricing
ERP pricing comes in two main forms: perpetual licensing with upfront costs or subscriptions with recurring fees. Cloud-based systems prefer subscription models. This approach cuts initial investment and includes ongoing maintenance and updates.
Several factors affect pricing: organization size, user count, customization needs, and deployment method. Cloud ERP costs less upfront than on-premises solutions, which leads to faster returns on investment.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems best use cases
ERP systems shine in several streamlined operations scenarios. Manufacturing companies use them to connect production processes and plan material requirements. Financial teams automate currency conversion and connect credit card processing with payroll systems.
Service organizations track their engagements and record activities as they happen. Global businesses use ERP to handle multiple currencies and keep their financial reporting consistent.
ERP systems remain vital for organizations that want to create truly integrated business operations. They connect every part of the enterprise into one efficient system.
Cybersecurity and Compliance Tools
Security is the foundation of integrated business operations. It protects digital assets and ensures regulatory compliance. Modern cybersecurity and compliance tools protect businesses from sophisticated threats without slowing down operations.
Cybersecurity and Compliance Tools key features
Today’s security solutions combine several key capabilities that protect integrated business operations:
Threat detection and monitoring scans for unusual activities and spots potential threats like malware or hacking attempts as they happen. This watchfulness helps organizations fix issues before they cause major damage.
Automated compliance checking reviews networks, tools, and processes against regulatory frameworks. The system spots non-compliant activities and notifies administrators to fix them. Organizations can stay aligned with industry standards this way.
Risk assessment finds weak points in systems and software to help prioritize fixes. This method puts resources where they matter most.
Access controls let organizations create and manage user privileges to stop unauthorized access to sensitive information. These detailed permissions keep data secure.
Centralized dashboards show quick snapshots of security and compliance health. You can see passing, failing, and critical checks in real time. This detailed view lets you tackle potential issues early.
Cybersecurity and Compliance Tools pros and cons
Pros:
- Helps meet regulatory requirements like HIPAA, SOC2, and GDPR
- Keeps sensitive information safe from data breaches
- Makes security monitoring automatic, which reduces mistakes
- Shows live updates for quick threat response
- Builds solid documentation for audits
Cons:
- Setup costs can be high, especially for detailed solutions
- People might rely too much on tools instead of seeing them as one part of security
- Tools need human oversight even with automation
- New systems take time to learn, which affects work speed at first
- Small businesses struggle as regulations expand and costs rise
Cybersecurity and Compliance Tools pricing
Security compliance software uses subscription models. Prices change based on organization size and needed features:
Basic cybersecurity tools cost $7 to $20 per user monthly. Management adds $12-$40, training costs $5-$15, incident response readiness is $10-$30, and regular security audits are $8-$25. The total might reach $42-$130 per user monthly.
Large companies get custom pricing based on their needs, like how many devices they monitor and which compliance rules they follow.
Cybersecurity and Compliance Tools best use cases
These tools work great in several business operations technology situations:
Healthcare groups use them to protect patient data and follow HIPAA rules. Banks need them to protect financial information and meet industry standards.
Companies going digital use these tools to build security into their integrated business operations from the start. Teams working remotely also need them to protect scattered systems and devices.
These tools act as a shield for business operations solutions. They make sure businesses can work efficiently while staying secure and following rules.
Employee Training and Onboarding Platforms
Image Source: Quixy
Modern training platforms have become a vital part of integrated business operations. These digital solutions automate learning and ensure consistent knowledge transfer throughout organizations. What started as simple course delivery has evolved into complete systems that blend naturally with existing business technology.
Employee Training and Onboarding Platforms key features
The most successful training platforms provide several core capabilities:
Automated workflows reduce errors and simplify repetitive tasks like document verification and scheduling. This frees up HR staff to focus on strategic work. Customization options let organizations create unique onboarding experiences that match their company culture and reflect their core values.
Interactive training modules use game elements to increase participation. Studies show 83% of employees feel more motivated when their training includes game-like features. Mobile accessibility lets employees complete important onboarding tasks from anywhere, which works well for remote and hybrid teams.
Self-service portals give new employees quick access to documents they need. This saves time for both HR and staff while letting employees learn at their own speed. Compliance management features automatically track documents to keep organizations ready for audits and protect them from legal risks.
Employee Training and Onboarding Platforms pros and cons
Pros:
- Fills skill gaps through focused training programs
- Makes learning fun through games, which increases participation up to 75%
- Boosts product knowledge across departments for better customer service
- Speeds up employee onboarding by up to 60%
Cons:
- High implementation costs for licenses and staff training
- Learning curves might slow down productivity at first
- Some employees resist changing from traditional training methods
- Regular updates and maintenance need dedicated resources
Employee Training and Onboarding Platforms pricing
Most platforms offer subscription-based pricing with different tiers:
Companies can pay per user, which helps them scale as they grow. Some platforms charge flat monthly fees whatever the user count. This makes costs predictable but might not be economical for smaller teams.
Free or freemium options exist, but they often have paid features that can quickly add up. Large enterprises usually get custom pricing based on their specific needs.
Employee Training and Onboarding Platforms best use cases
Fast-growing organizations use these platforms to create standard onboarding processes that work well even as hiring increases. Companies with remote teams rely on mobile-friendly training to keep standards high across locations.
Regulated industries need these tools to keep compliance training current and well-documented. Any business that wants to organize knowledge transfer and keep employees longer will benefit from these business operations solutions.
Comparison Table
Comparison of Integrated Business Operations Tools
| Tool Type | Key Features | Main Benefits | Primary Limitations | Typical Use Cases | Pricing Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Process Automation Tools | – IT Process Automation (ITPA) – Business Process Automation (BPA) – Robotic Process Automation (RPA) – Digital Process Automation (DPA) | – 80% reduction in manual workload – 30-40% reduction in process time – Error elimination – Better scalability | – High upfront investment – Complex setup – High maintenance needs – Limited flexibility | – Finance & Accounting – HR processes – IT operations – Customer Service | $15-750/month depending on package |
| Cloud-Based Collaboration Platforms | – Up-to-the-minute collaboration – File sharing & storage – Integrated communication – Version control – Access control | – 35% improved efficiency – Better communication – Economical solutions – Flexibility – Scalability | – Internet dependency – Security concerns – Learning curve – Decision-making delays | – Remote work – Cross-departmental projects – Client collaboration – Document management | $5-20/user/month with enterprise custom pricing |
| Integrated CRM Systems | – Contact management – AI-powered features – Third-party integrations – Up-to-the-minute data analysis – Mobile compatibility | – Unified platform – Automated tasks – Better customer experience – Better close rates | – Limited customization – Vendor dependency – Ongoing subscription costs – Data quality issues | – Sales operations – Marketing campaigns – Customer service – Lead management | Varies by vendor; subscription-based |
| Business Intelligence Tools | – Data visualization – Advanced analytics – Up-to-the-minute processing – Self-service analytics – Increased analytics | – Better data clarity – Improved efficiency – Better customer insights – Competitive advantage | – High setup costs – User resistance – Data skills gap – Security concerns | – Sales analysis – Customer analytics – Financial analysis – Supply chain optimization | $10-4,995/month depending on tier |
| ERP Systems | – Financial management – Supply chain management – HR management – Automation capabilities – Up-to-the-minute reporting | – Unified operations – Better collaboration – Up-to-the-minute visibility – Optimized processes | – High upfront costs – Long setup time – Security vulnerabilities – Complex customization | – Manufacturing – Financial operations – Professional services – Global business operations | Subscription or perpetual licensing; custom pricing |
| Cybersecurity & Compliance Tools | – Threat detection – Compliance checking – Risk assessment – Access controls – Centralized dashboards | – Regulatory compliance – Data protection – Automated monitoring – Up-to-the-minute insights | – Substantial costs – False confidence risk – Requires human oversight – Learning curve | – Healthcare security – Financial institutions – Remote workforce security – Digital transformation | $42-130/user/month for detailed solutions |
| Employee Training Platforms | – Automated workflows – Interactive modules – Self-service portals – Compliance management – Mobile accessibility | – Reduced onboarding time – Better participation – Consistent training – Better compliance | – High setup costs – Learning curve – Employee resistance – Ongoing maintenance | – Rapid growth companies – Remote workforces – Regulated industries – Knowledge transfer | Subscription-based with tiered pricing |
Conclusion
Conclusion
Integrated business operations need careful technology implementation rather than random adoption of trending tools. Our analysis shows how these seven tools solve specific operational challenges and improve overall business efficiency.
Companies that use process automation tools cut manual workload by 80% or more, though the upfront costs can be high. Cloud collaboration platforms make teams 35% more productive with real-time capabilities, despite possible internet connectivity issues.
The most effective strategy combines multiple tools into a unified integrated business operations approach. A CRM system builds the customer data foundation that business intelligence tools analyze. ERP systems help this information flow naturally between departments.
Building integrated business operations requires strong security measures. Cybersecurity tools guard your operational ecosystem from threats and ensure regulatory compliance. They work like an immune system for your digital infrastructure.
Your team needs proper training platforms to use these advanced systems well. These platforms bridge skill gaps and create consistent knowledge across your organization.
Companies should complete these steps before implementing any integrated business operations tools:
- Identify specific operational bottlenecks
- Calculate potential ROI against implementation costs
- Think over integration capabilities with existing systems
- Plan for appropriate staff training and change management
The right mix of these seven tools creates a technology foundation that accelerates growth, improves customer experience, and gives you a competitive edge. Despite implementation challenges, organizations that carefully adopt these integrated business operations solutions set themselves up for success in our increasingly digital business world.

